Plant Network Design
We have extensive experience in defining and further developing plant networks jointly with our clients resulting in a new level of performance
Our approach
Plant network design is an essential building block in the development of a winning manufacturing strategy

Driving forces
What is driving the plant network design?
Regulatory Environment
- Clinical development and production is moving to a continuum
- Fast track, breakthrough therapy, accelerated approval, priority review: pharmaceutical quality / CMC will be on the critical path
- Intensified and accelerated global data exchange
Science and Technology
- Drug / diagnostic combinations
- Gene editing with TALE and CRISPR/cas9 technologies
- Continuous production for small and large molecules
- Vertical / horizontal integration in a plant and for the entire network
- Alternative production by e.g. 3D printing, autonomous robots and systems
Political/Social Environment
- Increasing price pressure in all regions and key countries
- Clear request for local value creation
- Country-specific and continuously tightened GxP requirements
- Global shortage of talent
- Digital natives with changed customer behavior
In general, site decisions are long-term binding – they must consider the political, social, and regulatory environment, top strategic technology and science trends as well as business requirements regarding market access and capital productivity.
A plant network must also be flexible with respect to long-term demand development and volatilities as well as robust against external changes of varying proportions – incremental and revolutionary – and caused by different drivers.
Starting point of design process
The plant network design starts with a simplified picture of the future landscape – creation of site categories.
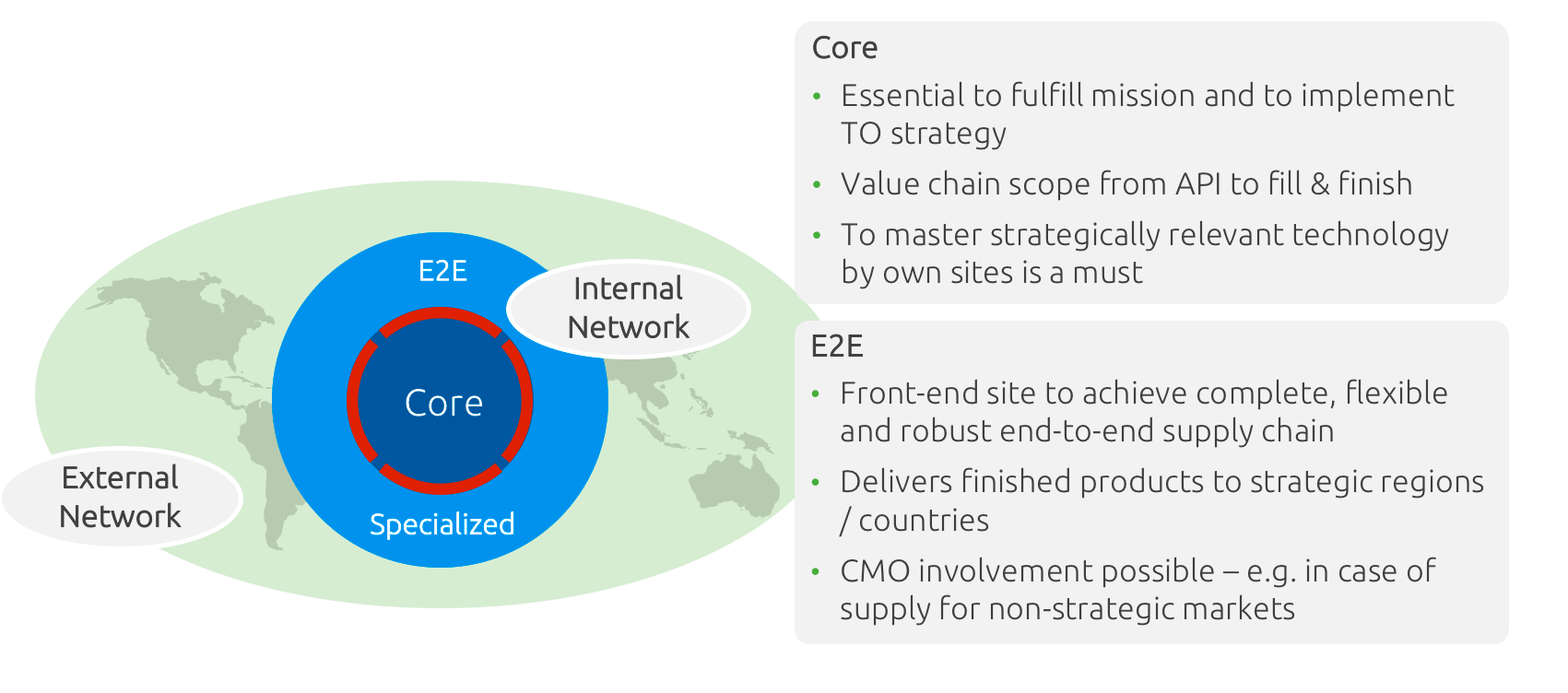
A clear set of criteria allows transparent allocation of sites to categories
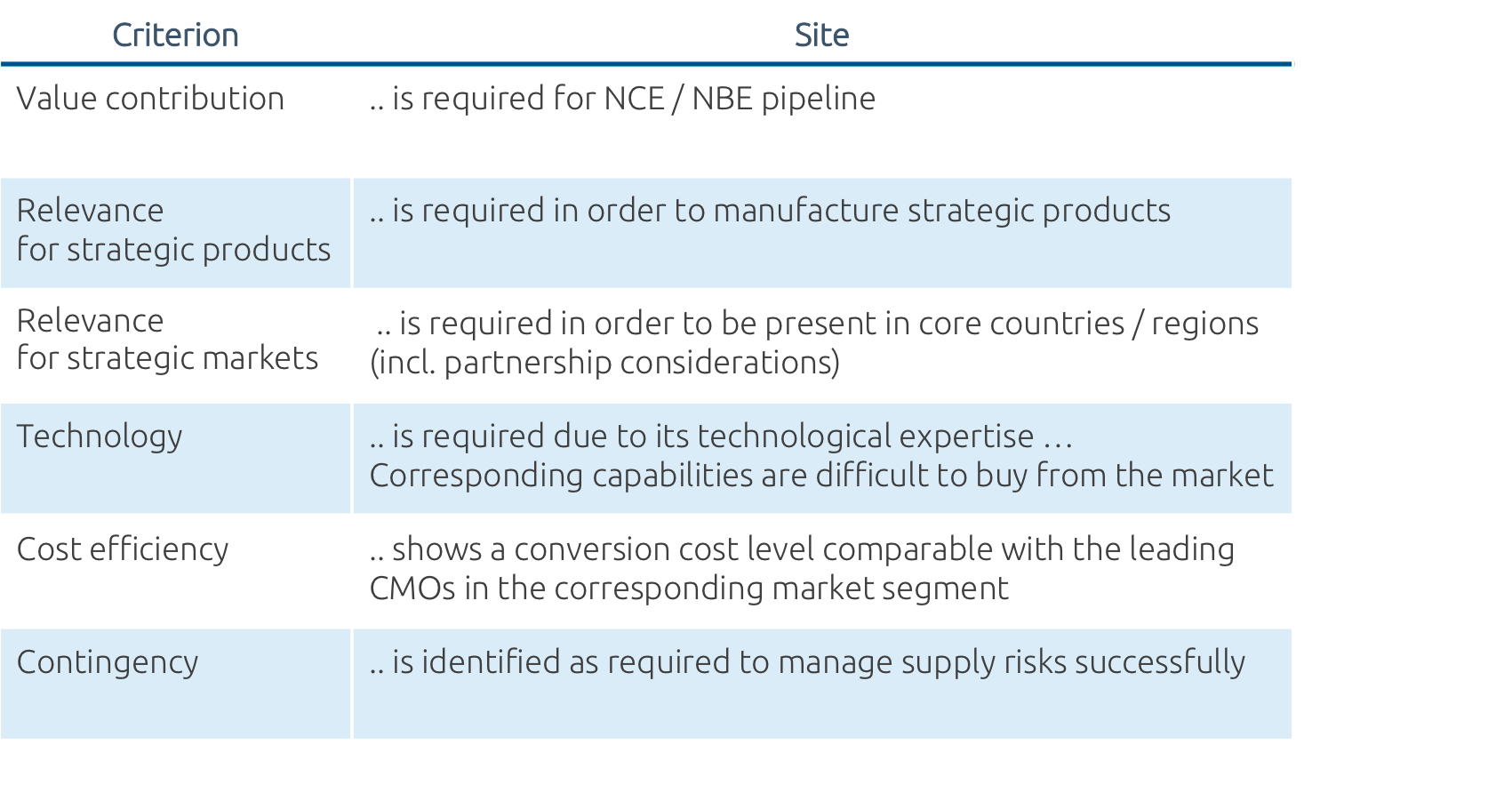
Other design principles worth bearing in mind
Risk mitigation and contingency considerations are essential elements of the network design process.
The network should reflect opportunities offered by the technological progress – e.g. scalability via scale-out and not scale-up, continuous production concepts, modular facilities, truly integrated end-to-end supply chain, unmanned plants.
A competitive advantage can be created by using such technologies.
In the case of innovative manufacturing technologies, site decisions should also consider the general innovation power of the environment as well as access to skilled and experienced staff.
Last but not least the entire plant network must find an optimum regarding CoGs development and overall CapEx requirements

Automotive Production Network Strategies - Lessons Learned for the Pharma Industry

